Best 8 Linux Partition Managers will be described in this article. In Linux, are you trying to manage or edit your disk partitions? The best disk management and partitioning tools for Linux users are listed in this article. Let’s start by defining disk partitioning and discussing its purposes.
Best 8 Linux Partition Managers To Create And Delete Disk Space
In this article, you can know about Linux Partition Managers here are the details below;
What is Disk partitioning?
The process of creating several logical storage units, or partitions, on a hard disk drive or solid-state drive is known as disk partitioning.
A partition is a portion of the hard disk that the operating system treats differently from other parts of the drive. The operating system views each of these partitions as a distinct disk with a unique file system and amount of storage.
A “partition table,” which has details on the size, type, location, and file system of each partition, serves as a unique identifier for each partition.
Different formats, such as MBR (Master Boot Record) or GPT (GUID Partition Table), can be used to build these partition tables. It is entirely dependent upon the constraints and requirements of the system.
Reason to perform disk partitioning
As an illustration, it enables you to divide data into several categories, such as personal files on one partition and the operating system and apps on another.
Partitioning also allows many operating systems to be installed on a single machine, each on its own partition. Dual-booting is the term for this technique, which also gives you the option of selecting the operating system to use when your computer boots up.
Either third-party software or the built-in utilities included with your base operating system can be used for this. It’s crucial to remember that data loss may occur from partitioning a disk. Consequently, before making any changes, you must backup any vital files.
What are Partition managers?
Software applications called partition managers let you control and work with the partitions on your hard disk.
A partition manager allows you to:
- To improve administration and organization, partition your hard drive into several sections.
- To maximize the use of available disk space or to provide additional room for a particular partition, resize or rearrange partitions.
- Partitions can be made or removed. For instance, to free up space for the installation of a new operating system or to delete an unnecessary partition.
- Partitions can have all of their data erased or formatted to make them usable.
- Alter the type of partition, for example, switching from a primary to a logical partition or the other way around.
Partition managers can operate independently on your computer or they can be incorporated into operating systems, backup and recovery programs, and other software tools.
IT specialists and system administrators who need to maintain and manage the hard disk partitions on their computers for a variety of reasons usually employ them.
When choosing the best partition manager, there are a number of things to take into account. Among them are:
User interface
A GUI is used by some partition managers, whereas a command-line interface (CLI) is used by others.
Beginners may find GUI-based partition managers to be a better option because they are typically easier to use.
Although CLI-based partition managers are more capable and often have more features, they may be more difficult to use for people who are not comfortable with the command line.
Features
Disk partition managers come with varying functionality. While some solutions may be more sophisticated and have features like managing numerous drives or resizing partitions without losing data, others may be more straightforward and just provide the most basic partition management capability.
Compatibility
Always check to see if the partition manager you select works with the file system and your Linux distribution.
Stability and Reliability
Selecting a dependable partition manager is essential to reduce the possibility of data loss or system breakdowns. Seek for a partition manager that has a solid user base and a solid track record.
Support
Think about how supportive the partition manager is. Does the developer offer bug fixes and updates on a regular basis? Do you have access to a community forum or support channel in case you run into any problems?
These variables have been taken into account when ranking the best Linux partition managers. Now let’s get going!
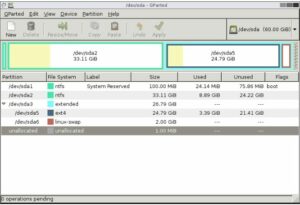
1. GParted
For Linux-based operating systems, GNOME Partition Editor, commonly referred to as GParted, is a free and open-source partition editor. This well-known program can be used to create, delete, and copy partitions as well as modify a partition’s file system type and label.
There are numerous file systems that may be created and modified with GParted, such as NTFS, FAT32, ext2, ext3, and ext4. Additionally, it has partition resizing and relocation functionality, enabling you to change the placement and size of partitions without erasing data.
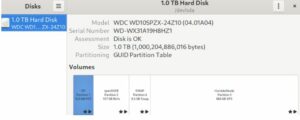
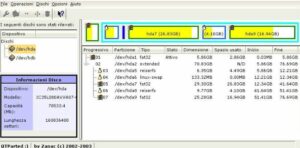
2. Gnome-disk-utility
On Linux computers, Gnome-disk-utility (Disks) is a graphical program that controls media and disc drives within the GNOME desktop environment. For managing storage devices, including as hard drives, solid-state drives, USB drives, SD cards, and other removable media, it offers a straightforward interface.
The user can benchmark performance, format disks, and adjust mount parameters among other disk management activities with this program. Moreover, disk images of whole disks or specific partitions can be made and saved in a variety of formats, including ISO, compressed, and raw.
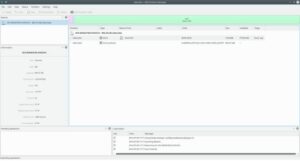
3. KDE Partition Manager
On Linux and Unix systems, KDE Partition Manager is a graphical user interface tool for managing disk partitions. Designed to be a component of the KDE desktop environment, it offered a user-friendly interface for partition creation, deletion, resizing, relocating, and copying.
The tool’s ability to integrate with the KDE desktop environment, which gives all KDE apps a unified appearance and feel, is one of its advantages. In addition, it offers several other capabilities like the capacity to make disk images and restore them, as well as the option to preview modifications prior to applying them.
It is updated and developed continuously. also boasts a robust user and development community that actively participates in its advancement and upkeep.
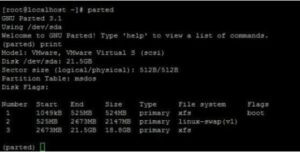
4. GNU Parted
For Linux and Unix systems, GNU Parted is an effective command-line tool for managing disk partitions. Partitions can be created, resized, moved, and deleted with it. It can also modify partition flags and provide lucid details about the disk and its partitions.
Parted’s ability to handle many partition table formats makes it a versatile tool that works with a range of file systems and platforms, which is one of its key advantages. It is compatible with popular partition table formats such as MS-DOS, GPT, BSD, Sun, and SGI.
Many file systems, such as NTFS, FAT16, FAT32, HFS+, ext2, ext3, and ext4, can be used with Parted. It can construct partition tables with many partitions and supports both main and logical partitions. This is another Linux Partition Managers. Also check Website Analytics Tools
5. NTFS-3G
Linux and other Unix-like operating systems can read and write data on NTFS (New Technology File System) partitions thanks to NTFS-3G, a free and open-source software driver.
On many Windows operating systems, NTFS is the default file system. Therefore, users who need to view files stored on NTFS partitions from within Linux or transfer files between Linux and Windows systems should have a driver like NTFS-3G.
Large files and partitions are supported, ownership and permissions are handled automatically, and it integrates with the Linux file system, among many other features.
6. QtParted
The Parted command-line utility has a graphical user interface called Qtparted. It was intended to be a copy of the Windows partitioning utility Partition Magic, which is a proprietary program. Additionally, it has some sophisticated capabilities like the capacity to do partition inspections and repairs and align partitions to maximize disk efficiency.
This program can run on a range of operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and Unix, because it is cross-platform and built on the Qt framework. It is mostly utilized on Linux and Unix systems, though, since software repositories or default installations frequently include it.
Since Qtparted is no longer being developed, it might not function properly on more recent or modern systems. Generally speaking, it is advised to use a more recent program, such GParted or KDE partition manager, which are updated frequently and offer more contemporary and dependable partitioning options. Also check Blogger Outreach Tools
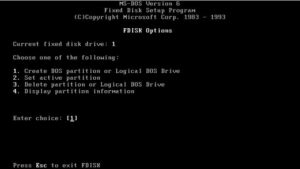
7. Fdisk
Popular command-line tool fdisk is used to manage partition tables on block devices, including solid-state and hard disk drives. On a disk, it enables users to create, remove, resize, and alter partitions. This is another Linux Partition Managers.
It is a widely used disk partitioning utility in Linux and other Unix-like operating systems. Fdisk is compatible with numerous file system formats, just like other partitioning programs.
The fdisk command’s fundamental syntax is as follows:
The hard drive device to be partitioned (such as /dev/sda) is specified here by “device,” and the command-line options that affect fdisk’s behavior can be specified by “parameters.”
Several frequently utilized fdisk parameters are as follows:
-n: Establish a fresh partition
-d: Eliminate a current partition
-l: Partial table list for the chosen device
-p: The partition table is printed.
-t: Modify the type of partition.
For instance, you can run the following command to make a new partition on /dev/sda.
fdisk /dev/sdasudo
The fdisk tool for the designated drive would launch as a result. From there, you can build, edit, and remove partitions as needed by using the different command-line arguments. This is another Linux Partition Managers.
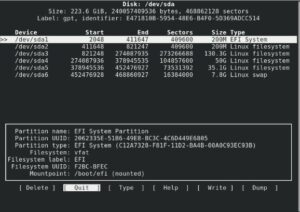
8. Cfdisk
An other partitioning tool for organizing partition tables on a disk is called Cfdisk. In addition, it is a command-line utility with an interface that is easier to use than fdisk.
Additionally, it offers a visual depiction of the drive and its partitions, making it simple for users to view the disk’s existing configuration and make necessary adjustments.
Note: Use partition manager tools with extreme caution as changing partition tables may cause data loss. Prior to making any modifications to the partition table on your hard disk, always make sure to backup any critical data.
Author’s note
To efficiently manage system resources, maximize disk space utilization, and organize data, partitioning a Linux system can be a crucial effort. To do this, Linux has a wide range of effective partitioning tools, both graphical and command-line based.
I hope this post has been useful to you in your search for the top Linux partition managers. You might also find it useful to understand how to partition a disk in Windows.