This post will explain what is a bug. Bug in software testing is defect or default in a component or system or software application that can cause the elements or system to fail to perform its necessary functions, in other information, we can say that if the bug or flaw came across during the execution of the search, it might trigger the failure of the components i.e. does not works as it expected from the parts. For instance, inaccurate data definition, statements, input information, style, etc
What is a Bug in Software Testing?
In this article, you can know about what is a bug here are the details below;
Live Process of Bug in Software Testing
The Bug Life cycle is also called a Defect Life cycle. It is a stage of a flaw that inhabits the various states throughout its life time. It begins when a screening gadget discovers a brand-new flaw and ends when the screening gadget gets rid of that defect and it is guaranteed that the problem is not replicated. It is now time to comprehend, through a basic diagram as shown below, the true workflow of a flaw life process. Also check Best free soundboard Reddit.
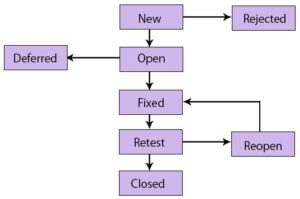
Below is the image of the Bug life process:
Let us see each element of the bug life process.
1. Open
The developer begins the bugs analysis process here, where possible, and works to fix it. If the developer believes that the flaw is not enough, then a mistake depending on the particular reason might be passed to the following four states, Reject or Not, particularly Duplicate.
2. New
This is the first state of bug category in the life process of the bugs. In the following stages of the bug life cycle validation & screening are performed on these bugs if a brand-new defect is discovered.
3. Assigned
The advancement team is assigned a recently developed fault for operating on the error at this level. This will be selected to a designer by the task leader or the team’s employer.
4. Pending Retest
Upon repairing the flaw, the designer will give the tester the fault for retesting the fault and the state of the problem stay in pending re-test’ up until the tester works on re-testing the fault.
5. Fixed
If the designer completes the task of fixing a problem by making the required changes, the flaw status can be called “Fixed.”. Also check defect management tools.
6. Validated.
If the tester has no difficulty with the error after the designer has been appointed the problem to the testing device and believed that if it was correctly fixed, the flaw status is appointed “confirmed”.
7. Re-open.
If there is still any difficulty with the flaw, the developer will then be advised to examine once again and the problem status will be reopened.
8. Closed.
If the problem is missing, the tester alters the flaw status to ‘Closed’.
9. Retest.
The tester then starts the job of re-testing the problem to examine whether the problem is correctly repaired by the developer as required by the requirement.
10. Replicate.
If the designer considers the flaw comparable to any other problem, or if the defect meaning mixes into any other flaw, the problem status is altered by the designer to ‘duplicate’.
Specification of Bug in Software Testing.
– Date of concern, approvals, author, and status.
– Severity and incident concern.
– The test case revealed the problem.
– Incident meaning with reproductive steps.
Assistance for Deficiency Life Cycle Implementation.
– The entire team must understand clearly the various conditions of a bug prior to starting the research study on the defect life cycle.
– To avoid confusion in the future, the flaw life process need to be documented effectively.
– Ensure that everyone with any job related to the Default Life Cycle comprehends his/ her duty for much better results really plainly.
– Every individual who changes the status of a flaw should know the status effectively which needs to provide enough info about the status of a defect and the reason for it so that everybody who works on that problem can easily see the factor for the problem.
– The flaw tracking tool ought to be managed with care in the workflow of the problem life cycle to make sure consistency between the problems. Also check ninite alternatives.
Conclusion.
I hope you’ve got some understanding of a flaw’s life cycle. This article will likewise assist you conveniently in the future if you deal with software defects.